In this article, we will delve into the functionalities of the STM32 TIMER, focusing on harnessing periodic interrupts, counters, and output compare mode. Understanding how to effectively use the STM32 TIMER is essential for achieving precise timing control and optimizing performance in your STM32 microcontroller projects

Things used in this project
Software apps and online services
1- STMicroelectronics STM32CubeMX
2- STMicroelectronics STM32CubeIDE
3- Proteus 8
TIMER Operation Modes on STM32 Microcontrollers
In this project, we delve into the diverse modes of TIMER operation available on STM32 microcontrollers, which are widely employed in embedded systems. We specifically investigate three fundamental TIMER modes: Periodic Interrupt, Counter, and Output Compare.
Periodic Interrupt Mode:
In the Periodic Interrupt mode, the TIMER is configured to generate interrupts at specified intervals. This functionality enables the microcontroller to execute tasks periodically, facilitating critical operations in embedded systems such as sensor readings, communication protocols, and time-sensitive tasks.
Counter Mode:
The Counter mode involves continuously tallying the occurrences of events within a predefined time frame. This capability is invaluable for applications like frequency measurement, pulse width modulation (PWM), and event monitoring, where precise event counting is paramount for system functionality.
Output Compare Mode:
Output Compare mode allows the TIMER to produce an output signal when its value matches a predetermined compare value. This mode is instrumental in generating precise timing signals, implementing PWM waveforms, and controlling actuators in various applications such as motor control, LED brightness modulation, and audio synthesis.
Through this project, you will learn how to program and utilize the TIMER module in these different modes on an STM32 microcontroller. The project includes simulation in Proteus, allowing you to test and verify the behavior of your TIMER code before implementing it in a physical embedded system.
STM32CubeMX Configuration:
- Open CubeMX & Create New Project Choose The Target MCU STM32F103C6 & Double-Click Its Name
- Go To The Clock Configuration & Set The System Clock To 32MHz
Configuration for the TIMER Periodic Interrupt Mode:
- Configure The GPIO Pins PB3 as Output Pin
- In the Categories tab, select the TIM3 & enable Internal Clock
- In the Parameter settings tab, set the (Prescaler=1000 & Counter Peroid 32000) The purpose of this settings is to generate a periodic time event with a 100ms interval

- In the NVIC settings tab, Enable TIM3 global Interrupt
Configuration for the Timer Counter Mode:
- In the Categories tab, select the TIM1 & enable ETR2 in “Clock Source” the clock source is an external pin (timer1 input pin ETR2) which is highlighted as PA12.
- In the Parameter settings tab, set the (Counter Mode =up & Counter Peroid=10 & Auto-reload preload= Enable)
- In the NVIC settings tab, Enable TIM1 update Interrupt
- Enable USART1 Module (Asynchronous Mode)
- Set the USART1 and USART2 communication parameters (baud rate = 9600, parity=NON, stop bits =1, and word length =8bits)
Configuration for the Timer Output Compare Mode:
- In the Categories tab, select the TIM2 & Enable Output Compare for Channel 2 and 4
- In the Parameter settings tab, set the (Prescaler=3200-1 & Counter Peroid 1000)
- In the Outpute Compare Channel 2 set the (Mode=Toggle on match & Pulse 200 & Output compare preload = Enable)
- In the Outpute Compare Channel 4 set the (Mode=Toggle on match & Pulse 400 & Output compare preload = Enable)
- Generate The Initialization Code & Open The Project In CubeIDE
STM32CubeIDE Configuration:
- Write The Application Layer Code
- stm32f1xx_it.c
- main.c
#include "main.h"
#include "stm32f1xx_it.h"
/* USER CODE BEGIN EV */
extern UART_HandleTypeDef huart1;
uint8_t END_MSG[50] = "Overflow Reached!! Counter Reset!!\n\r";
/* USER CODE END EV */
/**
* @brief This function handles TIM1 update interrupt.
*/
void TIM1_UP_IRQHandler(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN TIM1_UP_IRQn 0 */
HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart1, END_MSG, sizeof(END_MSG), 100);
/* USER CODE END TIM1_UP_IRQn 0 */
HAL_TIM_IRQHandler(&htim1);
/* USER CODE BEGIN TIM1_UP_IRQn 1 */
/* USER CODE END TIM1_UP_IRQn 1 */
}
/**
* @brief This function handles TIM3 global interrupt.
*/
void TIM3_IRQHandler(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN TIM3_IRQn 0 */
HAL_GPIO_TogglePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_3);
/* USER CODE END TIM3_IRQn 0 */
HAL_TIM_IRQHandler(&htim3);
/* USER CODE BEGIN TIM3_IRQn 1 */
/* USER CODE END TIM3_IRQn 1 */
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN 1 */
#include "main.h"
#include"stdio.h"
int main(void)
{
uint8_t MSG[10] = {'\0'};
uint8_t CounterTicks;
HAL_Init();
SystemClock_Config();
MX_GPIO_Init();
MX_TIM1_Init();
MX_TIM2_Init();
MX_TIM3_Init();
MX_USART1_UART_Init();
while (1)
{
//Timer Periodic Interrupt Mode
if(HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_0)== GPIO_PIN_SET)
{
HAL_TIM_Base_Start_IT(&htim3);
}
//Timer Counter Mode
else if(HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_1)==GPIO_PIN_SET)
{
HAL_TIM_Base_Start_IT(&htim1);
CounterTicks = TIM1->CNT;
sprintf(&MSG,"Ticks = %d ",CounterTicks);
HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart1, MSG, sizeof(MSG), 100);
HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart1, (uint8_t*)&"\n\r", 2, 2);
HAL_Delay(200);
}
else if (HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_2)==GPIO_PIN_SET)
{
HAL_TIM_OC_Start(&htim2, TIM_CHANNEL_2);
HAL_TIM_OC_Start(&htim2, TIM_CHANNEL_4);
}
else
{
HAL_TIM_Base_Stop(&htim3);
HAL_TIM_Base_Stop(&htim1);
HAL_TIM_OC_Stop(&htim2, TIM_CHANNEL_2);
HAL_TIM_OC_Stop(&htim2, TIM_CHANNEL_4);
}
}
}
Proteus Configuration :
- Open Proteus & Create New Project and click next

- Click on Pick Device
- Search for STM32F103C6 & SW-SPDT(switch) & LED_RED & Button & RES
- Click on Virtual Instruments Mode then choose VIRTUAL TERMINAL
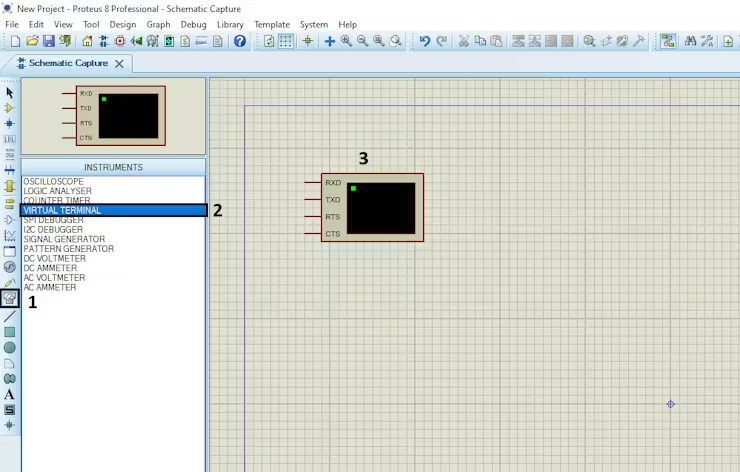
- Click on Terminal Mode then choose (DEFAULT & POWER & GROUND)
- finally make the circuit below and start the simulation
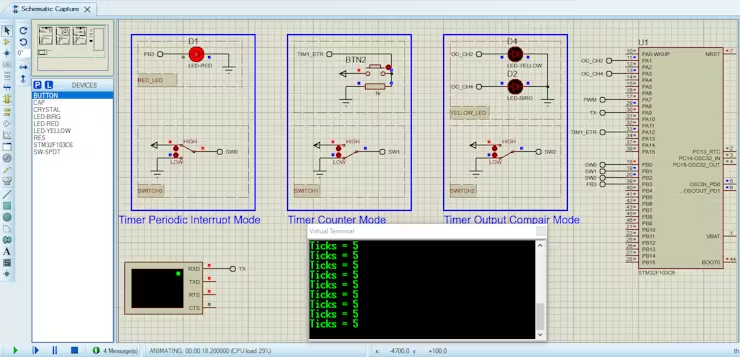
That’s all!
If you have any questions or suggestions don’t hesitate to leave a comment below.

1 comment
[…] the advanced Timer functionality offered by the STM32 series. By harnessing the capabilities of STM32’s Timer peripherals, developers can significantly enhance the accuracy and efficiency of distance […]